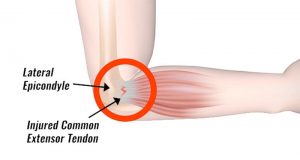
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a common condition that affects the tendons in the elbow, causing pain and discomfort. Despite its name, tennis elbow is not limited to tennis players and can occur in anyone who engages in repetitive arm motions. Often, flare-ups can occur from a simple weekend of gardening or cleaning.
Causes:
Tennis elbow is primarily caused by repetitive or strenuous activities that strain the forearm muscles and tendons. While tennis players often experience this condition due to the repetitive motion of their wrist and forearm, other activities such as painting, typing, gardening, or repetitive lifting can also lead to the development of tennis elbow. The repetitive motion causes tiny tears in the tendon, leading to inflammation and pain.
Symptoms:
The primary symptom of tennis elbow is pain and tenderness on the outer side of the elbow. The pain may gradually worsen over time and can extend down the forearm. Activities that involve gripping, lifting, or twisting motions, such as shaking hands, turning a doorknob, or lifting a coffee mug, may exacerbate the pain. Other symptoms include a weak grip strength and difficulty in fully bending or extending the arm.
Risk Factors:
While anyone can develop tennis elbow, certain factors can increase your risk, such as age, as the tendons can become less flexible and resilient over time, and participating in certain activities that require repetitive arm movements or gripping, like painting, carpentry, or playing musical instruments. Additionally, having poor technique or using improper equipment can also increase your likelihood of developing tennis elbow. Furthermore, playing tennis, golf or other racquet sports without proper form or conditioning of the muscles may also contribute to the problem.
Prevention:
To reduce the risk of developing tennis elbow, it’s essential to practice proper technique and form when performing repetitive arm movements. Making sure you’re using the proper equipment, such as rackets, golf clubs, or tools that are the correct size and weight for you, and reduced physical load can also be beneficial. Also, taking frequent breaks during activities that put a strain on your arms can help give your tendons time to rest and recover. Additionally, maintaining good overall physical health, staying hydrated, and incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine can also help prevent tennis elbow. Exercises that target the forearm muscles, such as wrist extensions and curls, can increase muscle strength and flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
Recovery Time:
The recovery time for tennis elbow can vary depending on the severity of the injury, the individual’s overall health, and whether the recommended treatment is followed carefully. With proper rest, modification of activities, and physiotherapy management, most people with mild to moderate tennis elbow should start to see improvement within six to eight weeks. However, severe cases may take longer to heal. It’s essential to follow the recommendations from your healthcare provider and avoid returning to your regular activities too quickly, as this can delay recovery and prolong your symptoms.
Treatment:
The first step in treating tennis elbow is to rest the affected arm and avoid activities that aggravate the pain, initially. Modifying your technique or using proper equipment, such as an ergonomic keyboard or racket, can help prevent further strain. Wearing a brace or forearm strap can provide support to the affected tendon and reduce strain during activities. A physiotherapist will prescribe specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the forearm muscles and tendons. These exercises can improve flexibility, reduce pain, and prevent future recurrences. In more persistent cases, extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) may be used to stimulate healing by delivering shockwaves to the affected area, promoting tissue repair. In rare cases when other treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be considered. The procedure involves removing the damaged part of the tendon and reattaching healthy tissue.
Conclusion:
Tennis elbow is a common condition that can affect anyone who engages in repetitive arm motions. It can cause pain and discomfort in the elbow and forearm, making everyday activities challenging. However, with early intervention and appropriate treatment, such as rest, modifications in technique, wearing supportive equipment, and specific exercises, most cases of tennis elbow can be resolved. If you’re experiencing symptoms of tennis elbow, it’s essential to seek the advice of a healthcare professional or physiotherapist who can provide an accurate diagnosis and create a treatment plan tailored to your needs. So don’t let tennis elbow hold you back. Take action and regain your freedom of movement.
An assessment from one of our team can get you steered in the right direction. Early intervention and physiotherapy management is often all that is needed to settle the condition.



Recent Comments